Behavioural
Economics
Session 14


Joshua
Foster

Agenda
- MobLab Simulation: Double auction market.
- Case: A Swift Pricing Decision.
Simulation instructions.
- The situation: there is a market for oranges for the class act as Buyers and Sellers in.
- What you do: make trades by negotiating on prices.
- Your objective: make trades in a way that maximizes your personal return.
How it works.
- Everyone is randomly placed in groups of 10.
- Within each grouping, each person is randomly assigned the role of either a Buyer or a Seller.
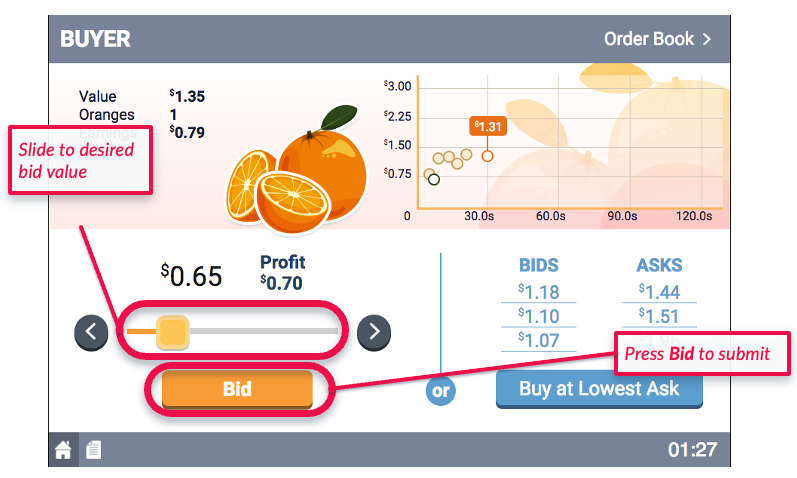
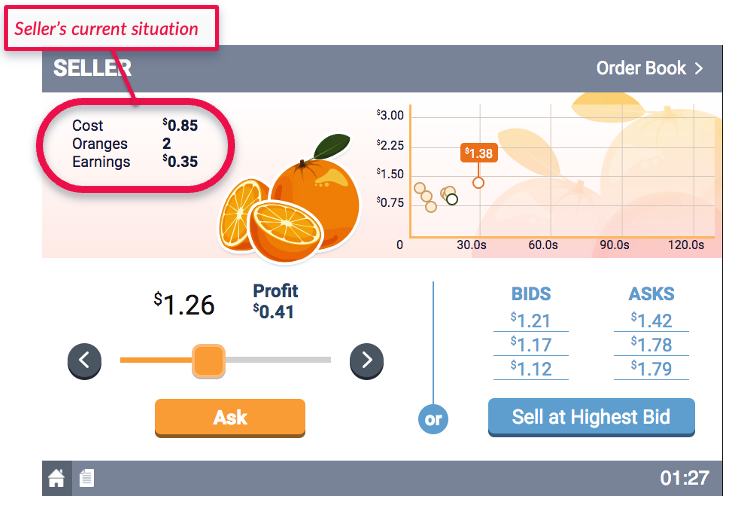
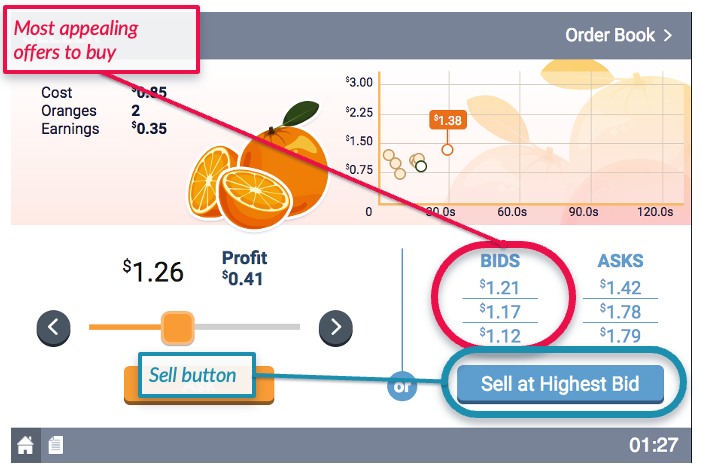
- The Buyers will make open bids, representing the prices at which they are willing to buy an orange.
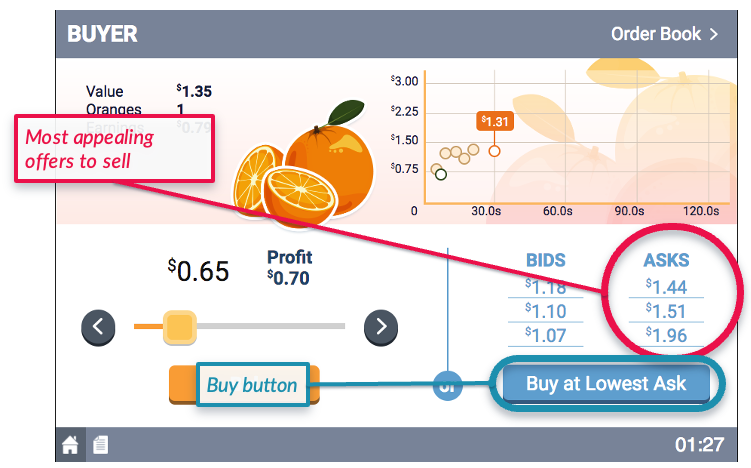
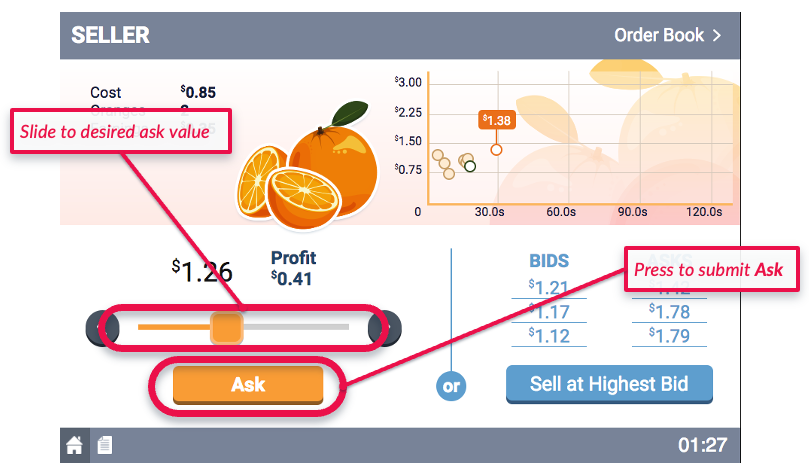
- The Sellers will make open asks, representing the prices at which they are willing to sell an orange.
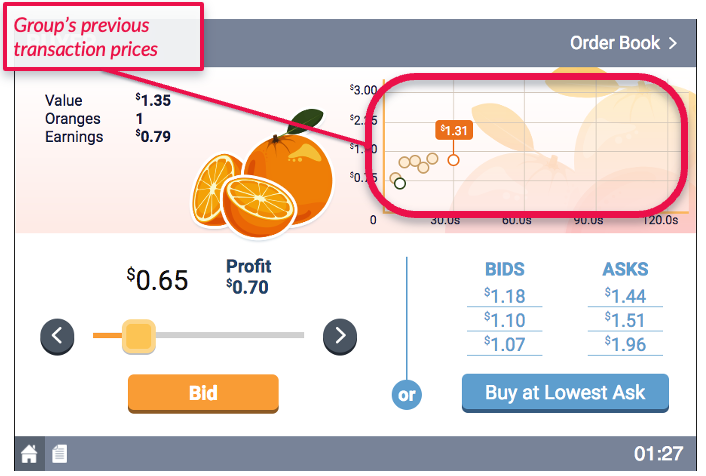
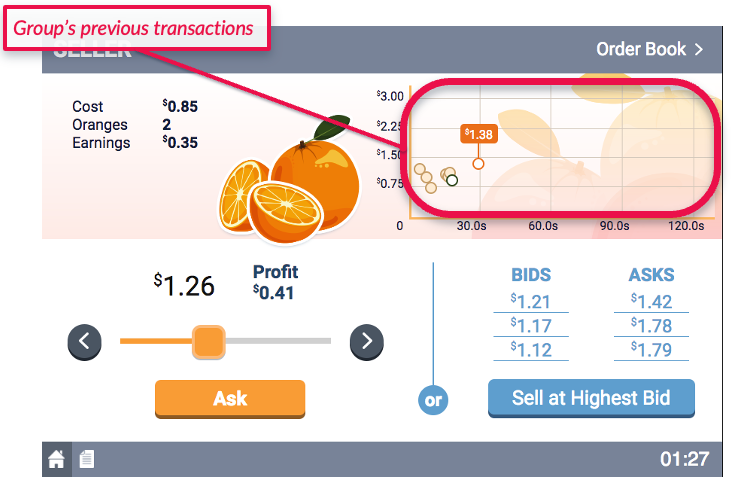
- Whenever the simulation finds a bid$\geq$ask in the market, it will execute the trade.
How do I decide my prices?
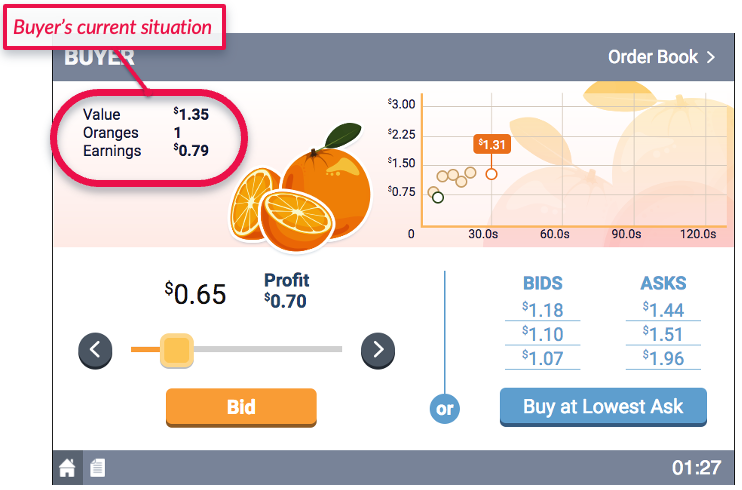
- The Buyers will have induced values for the oranges. That is, Buyers will be told the maximum they are willing to spend on a given orange.
- Likewise, the Sellers will have induced costs for the oranges. That is, Sellers will be told the least they are willing to accept for a given orange.
How you "win".
- The Buyers are seeking to maximize their consumer surplus (cs). That is, $\text{cs}=\text{value of orange}-\text{price paid}$ for each transaction.
- The Sellers are seeking to maximize their producer surplus (ps). That is, $\text{ps}=\text{price received}-\text{cost of orange}$ for each transaction.
Questions?
What was your pricing strategy?
Market equilibrium.
The price that ensures buyers and sellers want to buy/sell the same quantity (i.e. their market incentives are aligned).
What is Ticketmaster's business model?
How does Ticketmaster's dynamic pricing work?
What other markets use some form of dynamic pricing?
Surge Pricing.
A rapid increase in price that can be the result of a sudden increase in demand, decrease in supply, or the removal of pricing constraints (e.g. price ceilings).
“What do we want?”
— Justin Wolfers (@JustinWolfers) January 3, 2014
SURGE PRICING
“When do we want it?”
IN LONG-RUN EQUILIBRIUM#ASSA2014 pic.twitter.com/ugGx0HK0Ks
My friend was charged 18K for a 20 Min ride (!), and they are sticking to it. What in the world??? This is insane! @Uber_Support @badassboz @Uber pic.twitter.com/RjFihVLKIC
— Emily Kennard (@emilykennard) December 9, 2017
Ultimatum Game from Survey
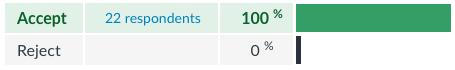
"Imagine I randomly and anonymously paired you with another student to negotiate how to split $10...[do you accept or reject the offer below?]
|
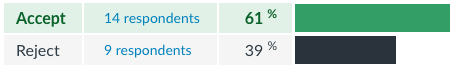
"Imagine I randomly and anonymously paired you with another student to negotiate how to split $100...[do you accept or reject the offer below?]
|
||||||||
|
|
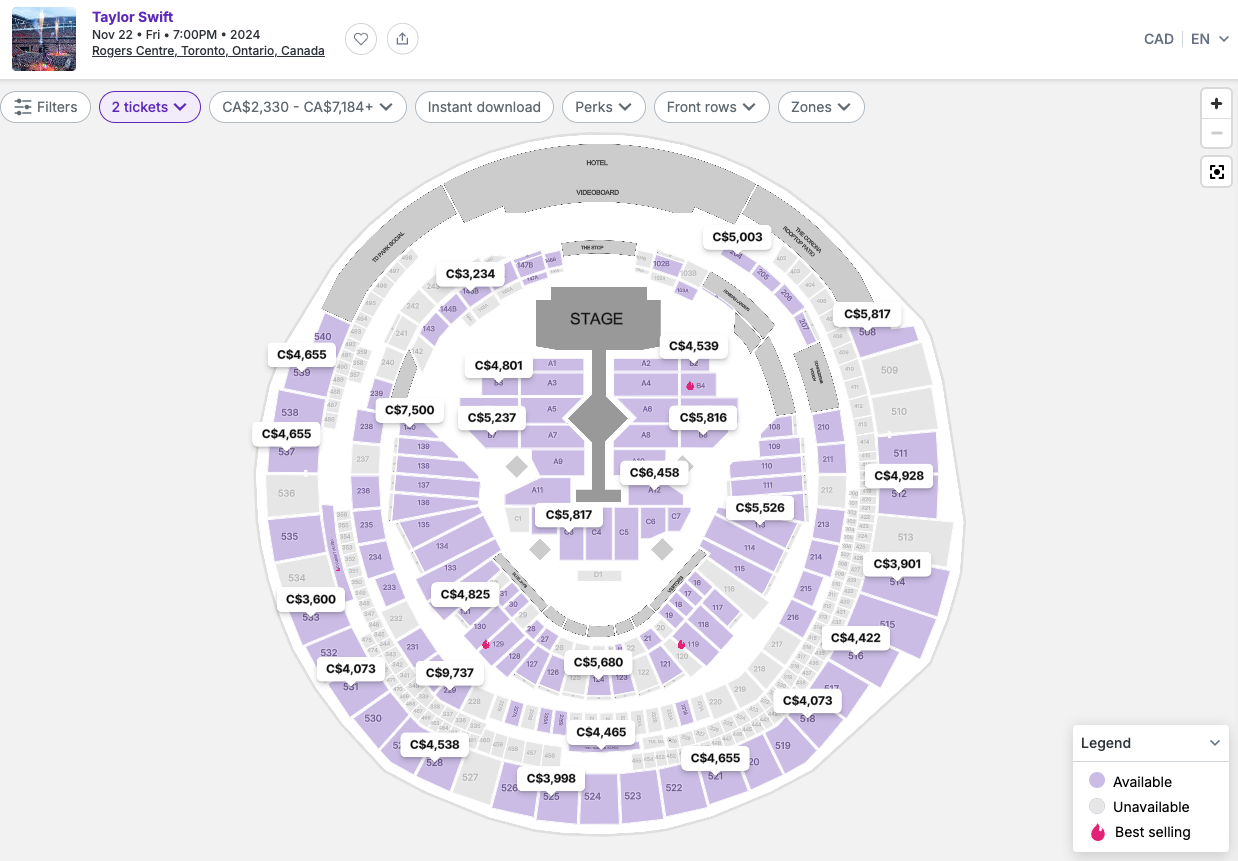
Which pricing model would you recommend Swift apply to her tour?
What are some strategies Swift could employ to manage her fans' behavioural reactions?
Market makers must account for non-price factors.
- Warm glow giving for non-profits.
- Distributional social preferences when comparisons to others are relevant.
- Reference points and loss aversion when comparisons to expectations are relevant.
Standard economic models will under-estimate the influence of these preferences on market outcomes.