Global Economy, Markets and Strategy

Agenda
- Case: Choosing a Price for Desdol.
- Marginal Analysis for Profit Maximization.
- Maximum Price Heuristic.
Describe the case's problem.
What price would recommend for Desdol?
Economist's objective: maximize profit.
- How do economists measure profit?
- How is their measure slightly different from other notions of profit?
Profit $=$ Revenue $-$ Cost
- Where does revenue come from?
- Where do economists get this information?
- Where do costs come from?
- Where do economists organize this information?
| Demand | Revenue Information | Cost Information | Profit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Quantity | Revenue | Marginal Revenue | Cost | Marginal Cost | Revenue - Cost |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 4 | 2 | 4 | ||||
| 3 | 3 | 8 | ||||
| 2 | 4 | 13 | ||||
| 1 | 5 | 19 | ||||
Optimal pricing with marginal analysis.
Select the price for which marginal revenue equals marginal cost ($MR=MC$).
- That is, select the price at which the money coming into the firm on the last unit is exactly equal to the money leaving the firm on said unit.
Regarding the case...
What makes applying marginal analysis difficult?
What are some alternatives to marginal analysis?
| 1) | 2) |
| 3) | 4) |
| 5) | 6) |
Maximum Price Heuristic.
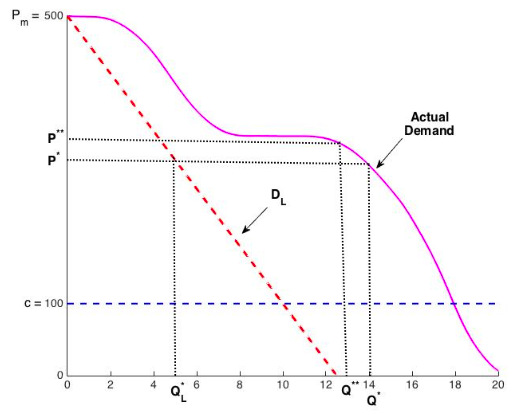
Select the price according to $P^*=(P_m+C)/2$.
- $P_m$ is the maximum price that still sells a few units.
- $C$ is the per-unit production cost (i.e. marginal cost).
See Cohen et al. (2021) in Management Science for details.
Cohen et al. (2021), Figure 1.
Cohen et al. (2021), Figure 5.
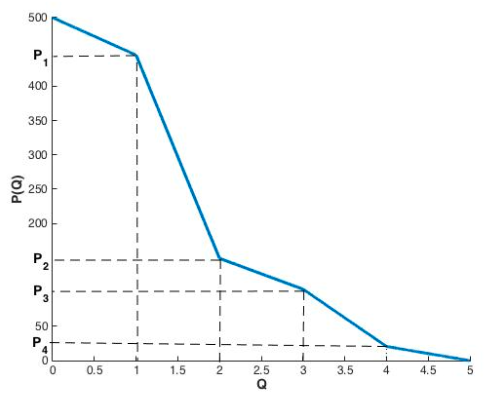
Among 100,000 simulations, this method assigned a price within 13% of the optimal profit over 80% of the time.
A few assumptions underlie this approach.
- The firm is able to estimate the maximum price, $P_m$.
- Marginal cost ($C$) is known and constant.
- The firm need not know the quantity it will sell.
Key takeaways.
- Demand curves give us information about where revenues come from and supply curves summarize our information about costs.
- A residual demand curve is the object that captures the number of units a firm will sell at each possible price, given the strategies of their competitors.
- Profit is maximized when a firm sets prices such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost ($MR=MC$).
- A useful alternative to marginal analysis is the Maximum Price Heuristic, which requires far less information.