Global Economy, Markets and Strategy

Agenda
- MobLab Simulation: Pick a Number
- Introduction to Game Theory
- Case: Pricing Games: Sony PlayStation and Microsoft Xbox.
- Duopoly Pricing Strategies
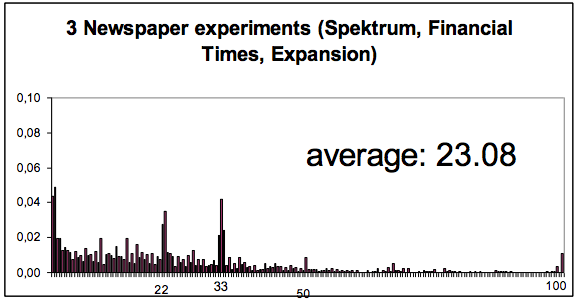
MobLab Simulation: Pick a Number.
Pick a number $X\in\{0,1,2,3,...,100\}$.
Objective: get closest to $\frac{2}{3}$ of the group's average.
Example: If you believe $\bar{X}=100\Rightarrow X^*=67$.
What is the rational way to play this game?
Every game has three components.
- Players endowed with game information.
- Strategies that are available to players.
- Outcomes that define players' payouts.
Level-k reasoning.
Individuals devise strategies according to their beliefs about others' rationality.
- L-0: Everyone else plays randomly.
- L-1: Everyone plays as if everyone else plays randomly.
- L-2: Everyone plays as if everyone else plays as if everyone else plays randomly...

What are the case's three game components?
- Players:
- Strategies:
- Outcomes:
Sony and Microsoft should look at:
- Contribution per unit
(price per unit $-$ average variable cost per unit) - Total contribution
(contribution per unit $\times$ number of units sold)
Why is the focus on profit over variable cost and not total profit?
Let's calculate the Contribution per Unit for both when $P_{\text{Sony}}=399$ and $P_{\text{Microsoft}}=399$.
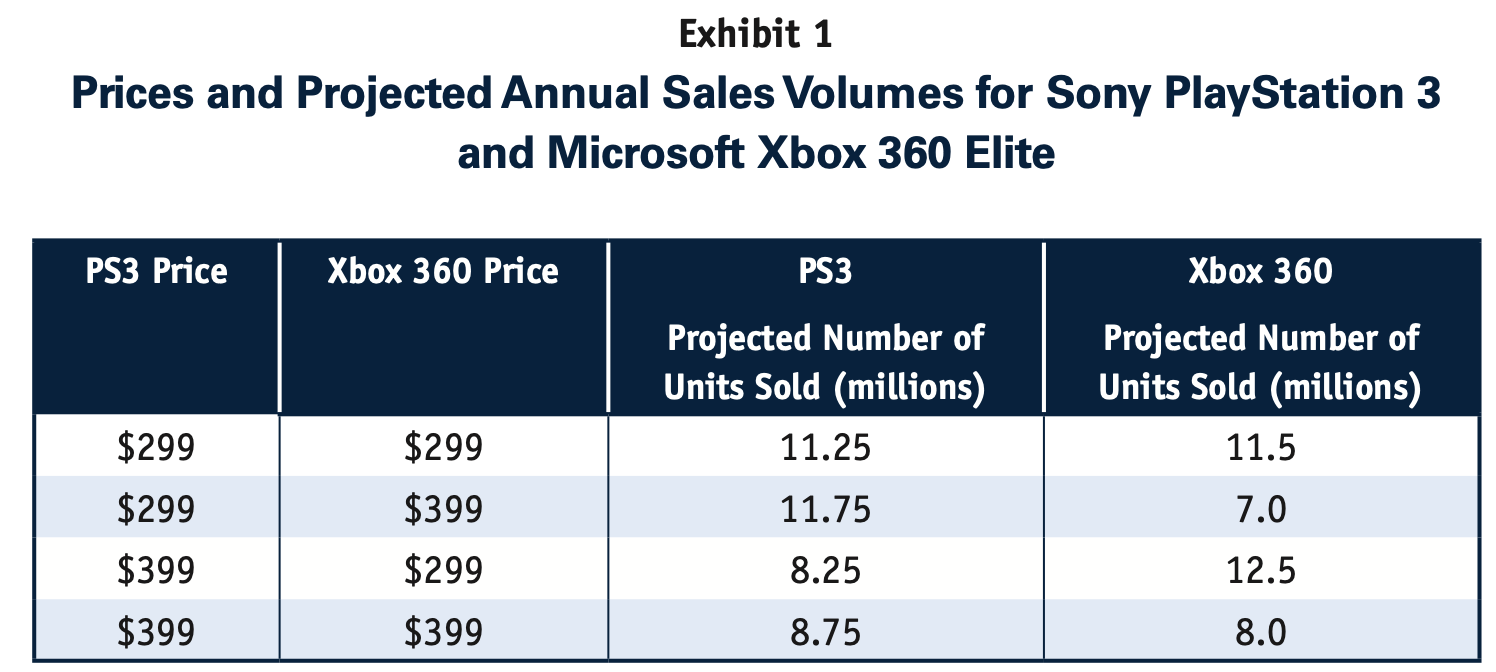
What is Sony's Variable Cost per Unit?
What is Microsoft's Variable Cost per Unit?
So what is Sony's Total Contribution?
And what is Microsoft's Total Contribution?
Let's calculate the Contribution per Unit for both when $P_{\text{Sony}}=399$ and $P_{\text{Microsoft}}=299$.

What is Sony's Variable Cost per Unit?
What is Microsoft's Variable Cost per Unit?
So what is Sony's Total Contribution?
And what is Microsoft's Total Contribution?
Summary of Players, Strategies and Outcomes
| Microsoft | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| $399 | $299 | ||
| Sony | $399 | 1032.5 | 960 | 767.3 | 1012.5 |
| $299 | 1186.8 | 637 | 978.8 | 920 | |
What should Sony and Microsoft do?
Nash Equilibrium
A combination of strategies in which no player has an incentive to unilaterally change what they are doing. In other words, all players are currently doing their best against all other players.
What type of game are Sony and Microsoft playing?
Prisoner's Dilemma
A game in which the Nash Equilibrium makes players worse off than they otherwise could have been with non-equilibrium strategies.
Why are Sony and Microsoft so aggressive in pricing their consoles?
A few possible explanations.
- Keeping Nintendo (or others) from gaining market share.
- Razor-razor blade pricing with (price discriminating) games.
- Achieving economies of scale.
- Predatory pricing now $\Rightarrow$ monopoly pricing later.
How might Sony and Microsoft break out of their Prisoner's Dilemma?
Final notes on case.
- In August 2009, Sony dropped its price to 299.
- Microsoft quickly followed suit.
- Nintendo held its price at 250 for an additional month, and then dropped it to 199.
Key takeaways.
- Firms' outcomes are inter-dependent according to their collective actions (e.g. pricing strategies).
- Markets settle into an equilibrium when all firms have selected a strategy they do not want to unilaterally deviate from.
- The equilibria in many markets will generate a Prisoner's Dilemma for firms due to the competition.