Global Economy, Markets and Strategy

Agenda
- Case: United Grain Growers Limited.
- Economics of Mergers.
- Merger Paradox: A Behavioural Explanation.
What does UGG do as a grain handler?


Who are UGG's competitors, and how do they stack up relative to each other?
Prior to the takeover bid, what did UGG do to prepare for a scaling grain market?
Should UGG fight this forced merger?
Economics of Mergers
- If there are no synergies, then mergers don't always benefit shareholders.
- We can demonstrate this by comparing the economic profits of a merger with a counterfactual -- the status quo.
What's happening here?
- The merged firms ultimately find it advantageous to reduce their output.
- The remaining market firm(s) respond by picking up some of the slack created.
- This tradeoff is what reduces the merged firms' combined profits.
Merger Paradox
Merged firms make less cumulative economic profit than they did as individual firms prior to the merger.
Even more survey question insights.
| If I picked a random student out of this class, what would you say is the probability that upon finishing their studies they will land a job with a starting salary over $120,000? | What do you think is the probability that upon finishing your studies you will land a job with a starting salary over $120,000? |
| $\bar{X}=62\%$ "Low, like this seems like very much." -someone | $\bar{X}=86\%$ "I think the probability will be up to 95%." -another "0%, lol" -yet another |
Ego utility.
Utility that is derived from beliefs about one’s traits and abilities.
- Entrepreneurs think their business is less likely to fail.
- 90% of drivers think they are better than average.
- Majority of professors think they are above average teachers.
Why shouldn't we expect managers to be over-confident?
Why should we expect managers to be over-confident?
What are the organizational symptoms of managerial overconfidence?
Managerial hubris can grow as:
- The trait becomes more important.
- Feedback on trait becomes more ambiguous.
- One believes they have more control.
- One is perceived to be an expert.
The Urge to Merge
- CEOs receive significant compensation in stock options.
- To minimize risk, they should exercise those options.
- If they don't, they are (arguably) overconfident.
Probability of Completing a Merger
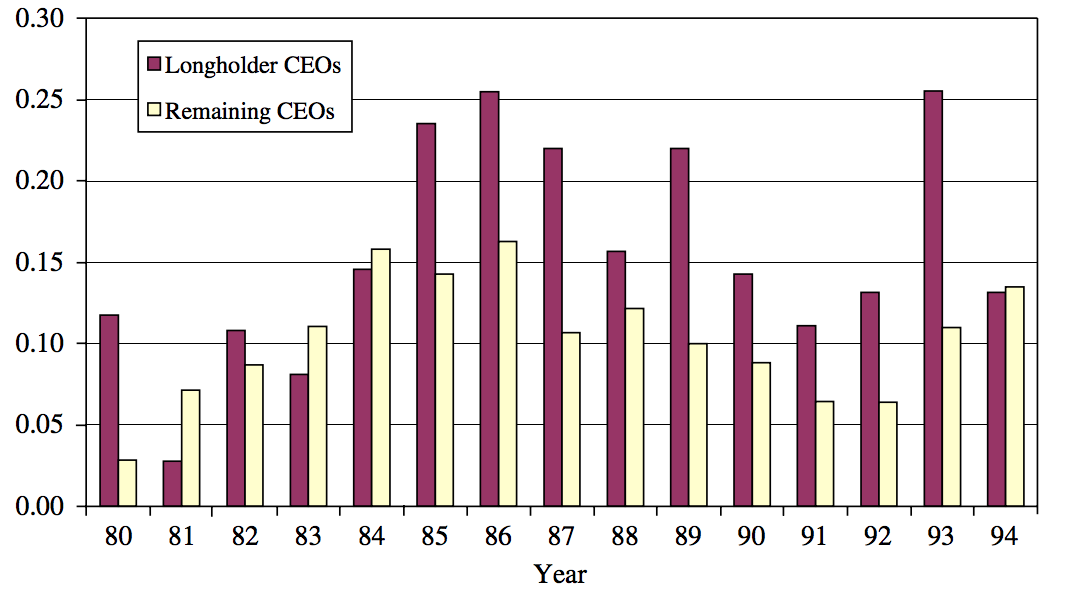
Malmendier and Tate (2008) in J of Financial Economics
What happened.
- UGG used a poison pill by going to court to block takeover.
- Found a "White Night" in Archer Daniels Midland, bought a 42% stake.
- In 1998, Alberta and Manitoba Wheat Pools merged to form Agricore Limited.
- Agricore bought UGG in 2001 via a stock swap.
Key Takeaways
- Firms and their CEOs often want to believe the benefits of merging outweigh the costs associated to doing so.
- The Merger Paradox theoretically and empirically suggest this benefit is over-stated relative to counterfactuals.
- Additionally, Ego Utility provides a behavioural explanation for why it can persist.